Blog
This is currently 2024 and having a reliable network is super important no matter you are setting up a business or just trying to keep things running smoothly at home. At the core of any strong network is something called structured cabling.
However It’s the setup that keeps all your devices connected and ensures they can communicate with each other without a hitch. So, let’s get right in and check out the main types of cabling that make these systems work so smoothly.
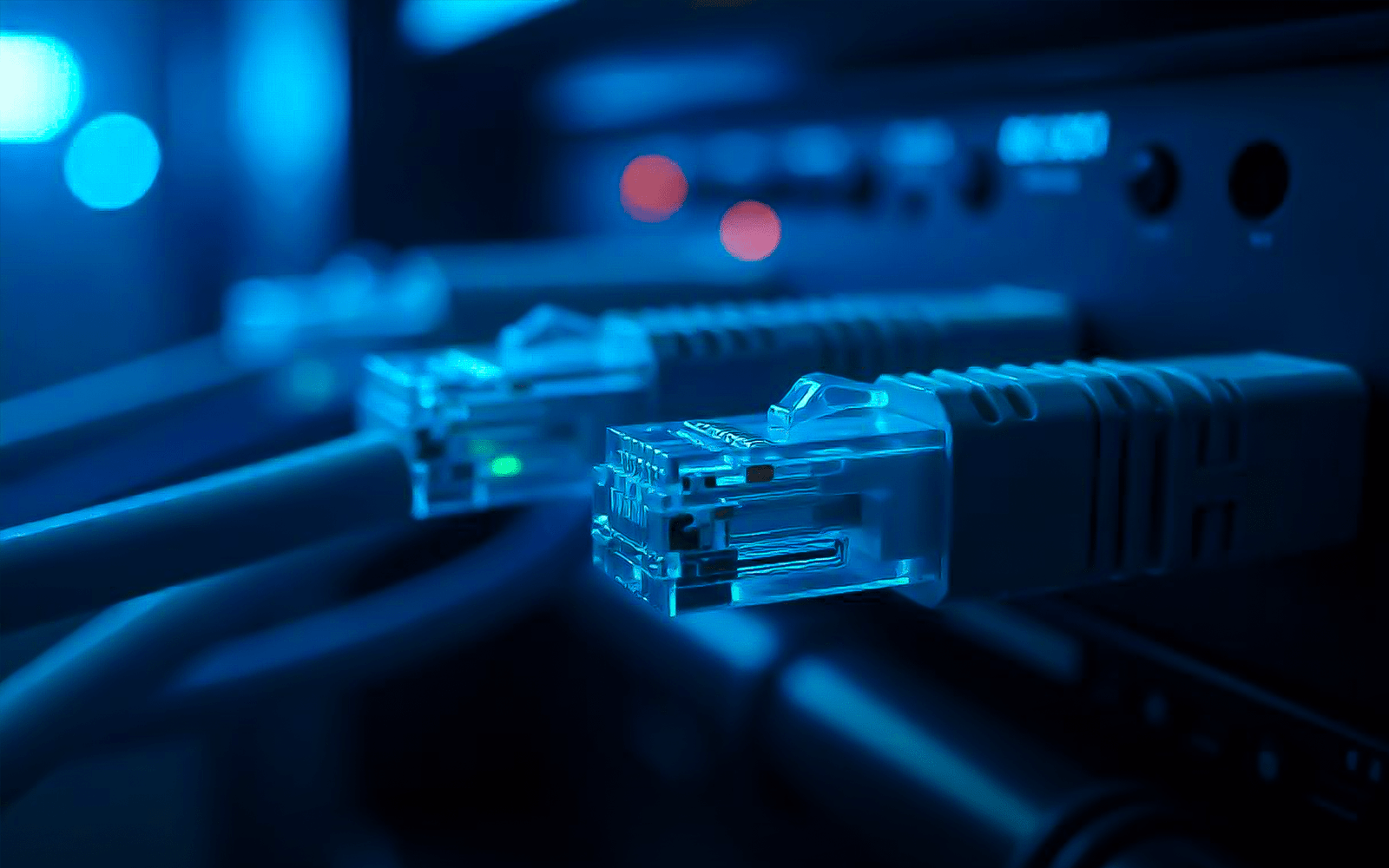
1. Ethernet Cables
Starting with the most common types of cabling which is Ethernet cables since these cables are the foundation of most local area networks (LANs). They link computers, routers and other devices within a network handling data transfer seamlessly. Ethernet cables come in several categories each offering unique speed and distance capabilities.

-
- Cat5e (Category 5e)
Cat5e is considered as the top choice for basic home and office setups as it supports up to 1 Gbps speed for distances up to 100 meters by providing a good balance of speed and affordability.
-
- Cat6 (Category 6)
A step up, this cable supports up to 10 Gbps but only for shorter distances (about 55 meters). This is a solid option for setups that demand faster data rates like offices with high data usage.
-
- Cat6a (Category 6a)
Great for data centers and high performance networks, Cat6a handles speeds up to 10 Gbps over a full 100 meters. It is designed for more intensive applications assuring a stable and high speed connection.
2. Fiber Optic Cables
Next, Fiber optic cables are known for their speed and range making them popular for large scale data transfers over long distances. In contrast to Ethernet which uses electrical signals, fiber optic cables rely on light to move data.

-
- Single Mode Fiber (SMF)
Designed for long distances, SMF has a narrow core that supports one light signal at a time minimizing interference and making it ideal for telecommunications or connections across cities.
-
- Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
With a larger core, MMF can carry multiple light signals allowing for high speed connections over shorter distances like within a building or across a campus.
3. Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are essential for reducing interference in network setups. They consist of pairs of copper wires twisted together with a couple of main types for different environments;

-
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
A quite usual pick in low interference areas like standard office spaces, UTP cables are affordable, easy to install and reliable for most Ethernet connections.
-
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
In areas with higher interference from nearby electronics or wiring, STP cables come with extra shielding to maintain data integrity giving them suitable for factories or environments with more electrical noise.
4. Coaxial Cables
If you have ever had cable TV or a broadband connection, you are likely familiar with coaxial cables. These cables feature a single copper core surrounded by insulation and shielding providing clear and consistent data transmission.
-
- Cable Television (CATV)
Coaxial cables are commonly used to deliver cable TV signals to homes and businesses offering reliable audio and video transmission.
-
- Internet Services
While fiber is taking over, many broadband providers still use coaxial cables in areas without fiber optic infrastructure providing an affordable internet connection.
5. AC Power Cables
AC power cables don’t carry data but are crucial for keeping your network devices running. They deliver electricity to routers, switches and other equipment. Organizing power cables properly and keeping them separate from data cables helps reduce interference and keeps your setup safe and clean.
6. Special Data Transmission Cables
In some cases, you will need cables that handle special conditions even if it is exposure to high levels of interference or outdoor environments.
-
- Direct Attach Copper (DAC) Cables
These are short, high speed cables often used to connect devices within close proximity such as between servers and switches. They offer full speed performance over very short distances making them ideal for data centers.
-
- InfiniBand Cables
Used in high performance computing, InfiniBand cables deliver fast speeds and low latency are critical for environments that require instant data processing such as research labs or data heavy industries.
Conclusion
So now you know that the right types of cabling really are key to building a network that works reliably. Each cable type has its own special job like Ethernet cables handle everyday data transfers, fiber optics take care of long distance connections and coaxial cables are perfect for video signals.
Picking the right mix does not just give you the speed and stability you need right now yet it also sets your network up to handle whatever the future brings.

